Authentication
Accessing the LanguageWire Project API requires a set of authentication credentials, that you must pass with each request.
Sandbox temporal tokens as well as App's credentials, can be obtained from our Dashboard.
OAuth 2.0 authorization
We use the OAuth 2.0 authorization framework for both the Basic endpoints that return generic data (/languages, /workareas, and /services) and for those retrieving private data (/account, /project and /files).
This is a standard protocol that provides security for our REST endpoints and it is widely used to protect access to APIs which are accessed by native applications and web applications.
All our operations require authentication that is performed on per-request basis. Such requests must include an authorization header composed according to the internal Bearer Token authorization schema:
authorization: Bearer Token {YourToken}
Bearer authentication
Bearer authentication (also called token authentication) is the HTTP authentication scheme that we apply to our API, and involves security tokens called bearer tokens. This is the most common way to access OAuth 2.0 APIs.
The bearer token is a single cryptic string, that acts as the authentication of the API request, sent in an HTTP “authorization” header.
| Header parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| authorization | Required - Valid access token following the format: Bearer <Access Token> |
The following example uses cURL to retrieve information about the list of users using the /get-users endpoint:
curl -L -X GET 'https://api.languagewire.com/project/v1/users'
-H 'Accept: application/json'
-H 'authorization: Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICJwdXpNZE5SUmVtOEN3emVxQ0RRdlZySGRpX29OZmF6ZTJ4V0EyLS1pelZJIn0.eyJleHAiOjE2Nzc1OTc2MjIsImlhdCI6MTY3NzU5NjQyMiwianRpIjoiN2UwOWU0NDUtNDAxMi00MjMwLWE0ZjItZTM3ZmJlNDFlM2YzIiwiaXNzIjoiaHR0cHM6Ly9pZHAubGFuZ3VhZ2V3aXJlLmNvbS9yZWFsbXMvbGFuZ3VhZ2V3aXJlIiwiYXVkIjoicGxhdGZvcm0tYXBpLWNsaWVudCIsInN1YiI6IjRkMjYwMDZlLTAzZjgtNDIxMi1iYTdmLWE4NjQ5MDBiMDc1ZCIsInR5cCI6IkJlYXJlciIsImF6cCI6Ijk2MDg5LXByb2plY3QtYXBpLXNhbmRib3gtYXBwIiwic2NvcGUiOiIiLCJDb21wYW55TmFtZSI6IlByb2plY3RzIEFQSSBTYW5kYm94IiwiY2xpZW50SWQiOiI5NjA4OS1wcm9qZWN0LWFwaS1zYW5kYm94LWFwcCIsImNsaWVudEhvc3QiOiIxNzIuMjkuMTUyLjEwMyIsIkNvbXBhbnlJZCI6Ijk2MDg5IiwiY2xpZW50QWRkcmVzcyI6IjE3Mi4yOS4xNTIuMTAzIn0.pqaI58fRpgJFz6D_bZWLjZQ1WeauBjYLAdb9-Q1MYi-Y05cWRodqdFAMhdlIL110op6YuUktjftPF35vPNwTs6wY-O63JIZqfPQZPcBngr5hp2irPVmWZ3e8eNBf62kVbLIUnhE94HPE8GQm2RaDq1MmsfgZS4qSCftL_GWPMCj5x3KnALgajspupVvJ1efs1K76vuv5t2_rycit49VwBHvXf-zINll6ptftTqpVBbARkfQsSYzSqvj2omJbzNy0FJ1VjIsH-lLBRAGMk0Iu09DWvrteu-zGS912NdIip1yUdy9MGG7wFcn1X4OYuZ5cAWvkxvyPX5bQG9ptaI9kxA
Client credentials flow
Client credentials are used as an authorization grant typically when the client is acting on its own behalf (being also the resource owner) or is requesting access to protected resources based on an authorization previously arranged with the authorization server.
In order to get your token from you integration application you just need to make a call to our identity provider as in this example:
curl --location 'https://idp.languagewire.com/realms/languagewire/protocol/openid-connect/token' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \
--data-urlencode 'client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID' \
--data-urlencode 'client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET' \
--data-urlencode 'grant_type=client_credentials'
Once you do that you will receive a response like:
{
"access_token": "eyJhbGc.....yv7kNw",
"expires_in": 1200,
"refresh_expires_in": 0,
"token_type": "Bearer",
"not-before-policy": 0,
"scope": ""
}
Then you can use this access token for the time in seconds it says in the expires_in.
Once the token is expired you can simply ask for a new one.
There are libraries that handle the client credentials OAuth 2.0 flow for you in different languages. For instance, for .NET, we can use the library Identity Model provided by Microsoft.
Generate credentials
Tokens
-
If you are using a sandbox account, you can generate your temporal token directly from the default sandbox entry, without the need of creating new applications.

-
If you have a production account with LanguageWire, you can also generate temporal tokens for your applications.
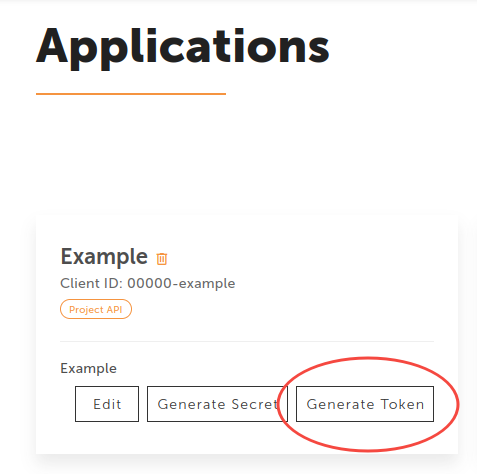
Secrets
If you have created your own application (that represents a confidential client) apart from tokens, you can generate what is known as client credentials, this is your application Secret.
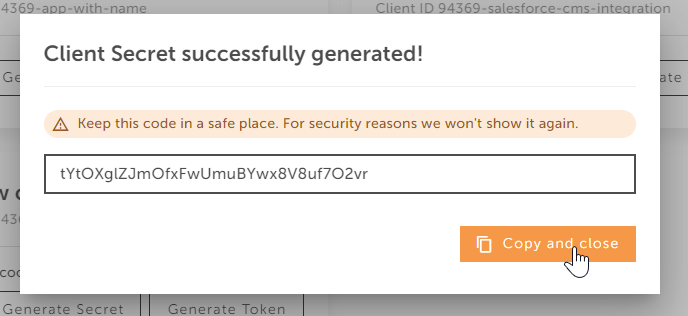
- Click on the "Generate secret" button to see the one time code.

Always store the client secret key securely; never reveal it publicly!
If you suspect that the secret has been compromised, regenerate it immediately by clicking the "Generate Secret" button again.
How to use the Token
To start making requests to our Project API, you should include the token in your API calls:
- Copy your generated token
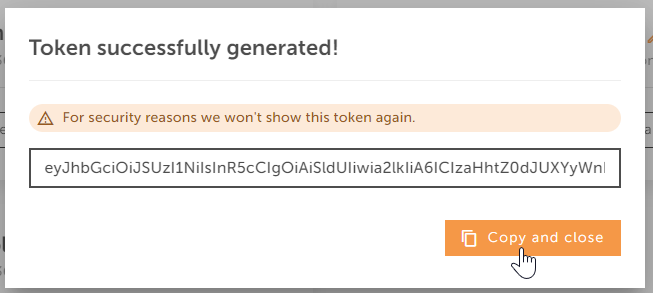
- Paste your token directly in the authorization request header.
-
Include the bearer token's access_token value in the HTTP request body as 'authorization: Bearer {access_token_value}'.
-
Example for the POST
/ProjectCreationrequest: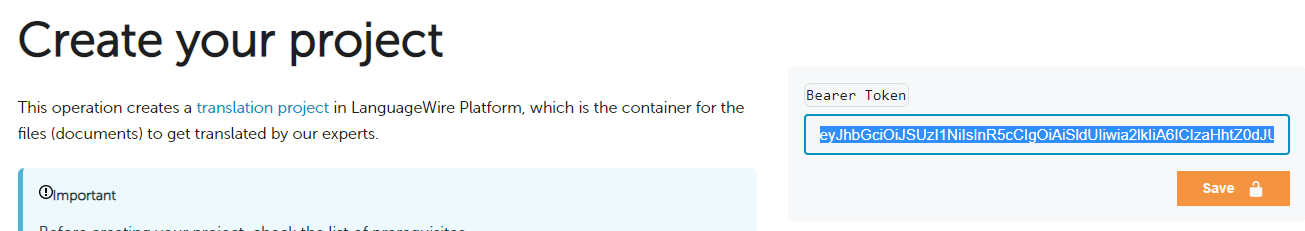
Unirest.setTimeouts(0, 0);
HttpResponse<String> response = Unirest.post("https://api.languagewire.com/project/v1/projects")
.header("Content-Type", "application/json")
.header("Accept", "application/json")
.header("Authorization", "Bearer eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsInR5cCIgOiAiSldUIiwia2lkIiA6ICIzaHh")
.body("{\n \"title\": \"string\",\n \"briefing\": \"string\",\n \"briefingForExperts\": \"string\",\n \"purchaseOrderNumber\": \"string\",\n \"deadline\": \"string\",\n \"templateId\": 0,\n \"serviceId\": 0,\n \"translationMemoryId\": 0,\n \"invoicingAccountId\": 0,\n \"userId\": 0,\n \"workareaId\": 0,\n \"externalId\": \"string\"\n}")
.asString();
Tokens are useful for testing purposes and short requests.